neuroscience
Neuroscience suggests that it’s way better to give than to receive — and high performing people agree.
The discovery has enormous implications for the development of novel anti-anxiety medications.
Neuroscientists hope to learn more in the hope of finding a way to reverse dementia.
Adolescents’ brains are highly capable, if inconsistent, during this critical age of exploration and development. They are also acutely tuned into rewards.
Forget these scientific myths to better understand your brain and yourself.
One hypothesis: “gossip traps.”
A study shows that the brains of lonely individuals respond in odd ways to visual stimuli, while those of non-lonely people react similarly.
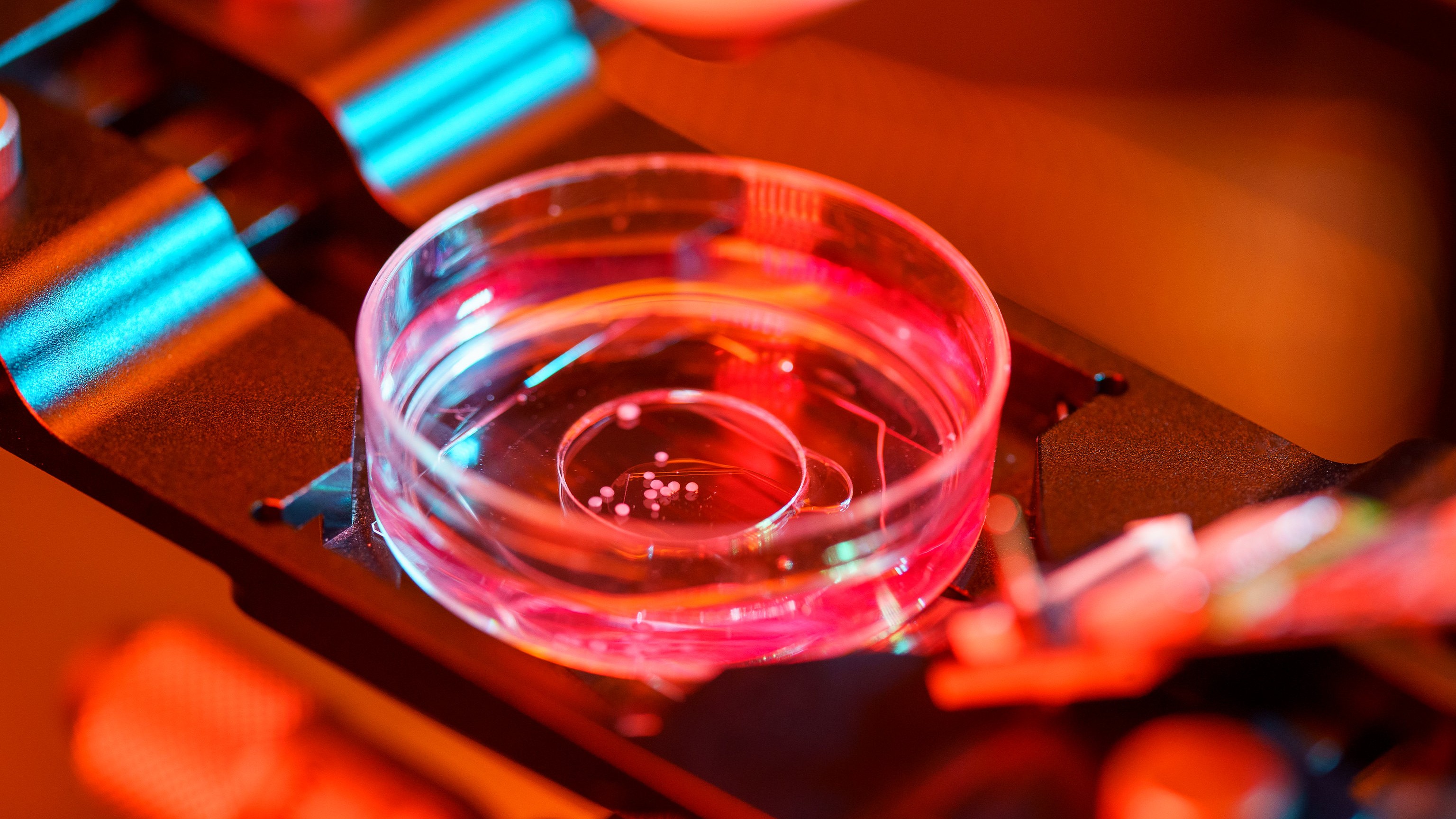
A recent study is the first to fabricate electronic components from endogenous molecules.
Research suggests parenthood helps couples tune into each other’s minds and emotional states.
The content of our long-term memories is constantly “reconstructed” by our brains. The same is true of memories formed mere seconds ago.
Our brainwaves naturally synchronize with external stimuli like flickering lights. Here’s how the phenomenon might boost learning.
The puzzle of play
The purpose of play — for children, monkeys, rats or meerkats — has proved surprisingly hard to pin down. Scientists continue to toss around ideas.
This was largely a philosophical question until 2005, when a surgical team in France performed the first partial face transplant.
Awe-inspiring moments can be found in our daily lives, and they have surprising benefits for our health and sense of well-being.
You know that ghostly feeling that someone is nearby even though nobody is? It could be a trick of neural timing.
Experimental neuroscientist Patrick McNamara on how we can harness spiritual experiences to explore alternate realities in our minds, and transform our models of the self.
▸
8 min
—
with
The study was small and didn’t include a placebo group, but there is reason to believe that the drugs really do work.
The ability to decode acoustic information from brain activity aids the development of brain-computer interfaces that restore communication in patients who suffer paralysis.
Tasting sounds and hearing colors.
A new study provides the most detailed look at brains on psychedelics to date.
Psychedelics mess with our prior beliefs, and could help us see what forms these beliefs in the first place.
If you’re trying to break a bad habit or start a good one, psychologists have some tips.
“It doesn’t erase what happened to you. It just changes the impact it has on your life.”
This is the latest study to confirm that the brain does not fully mature until at least the third decade of life.
Pick up the paintbrush and get to work.
As Abraham Lincoln famously said, “If you want to test a man’s character, give him power and a plate of cookies.” (Something like that.)
The simulation hypothesis is fun to talk about, but believing it requires an act of faith.
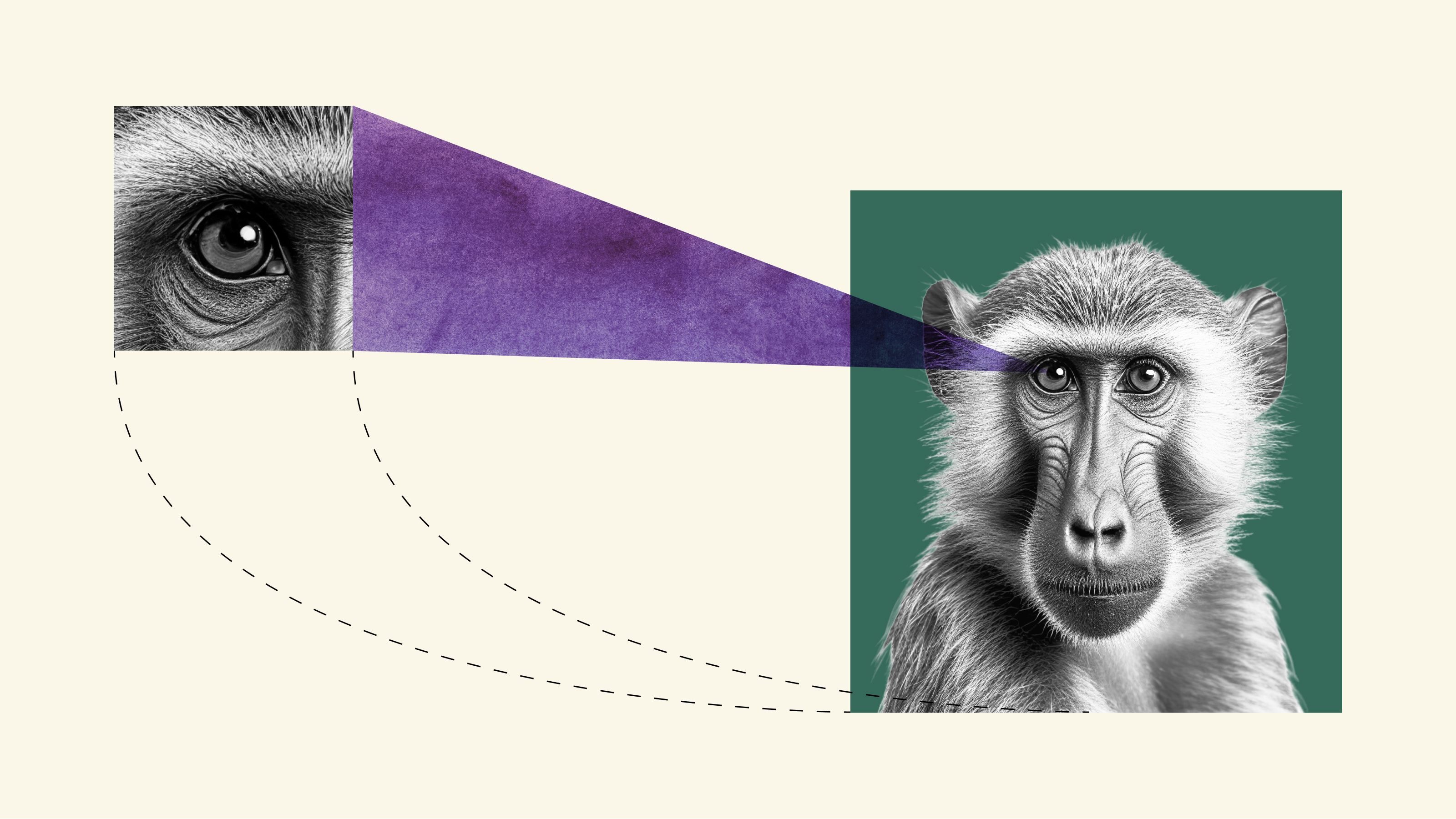
In all mammals, there are two brain pathways for processing information from the eyes: an evolutionarily ancient one and a more modern one.
Depression might be similar to dreaming.
Some scientists think brain organoids could develop a form of consciousness. Others say that’s science fiction.