neuroscience
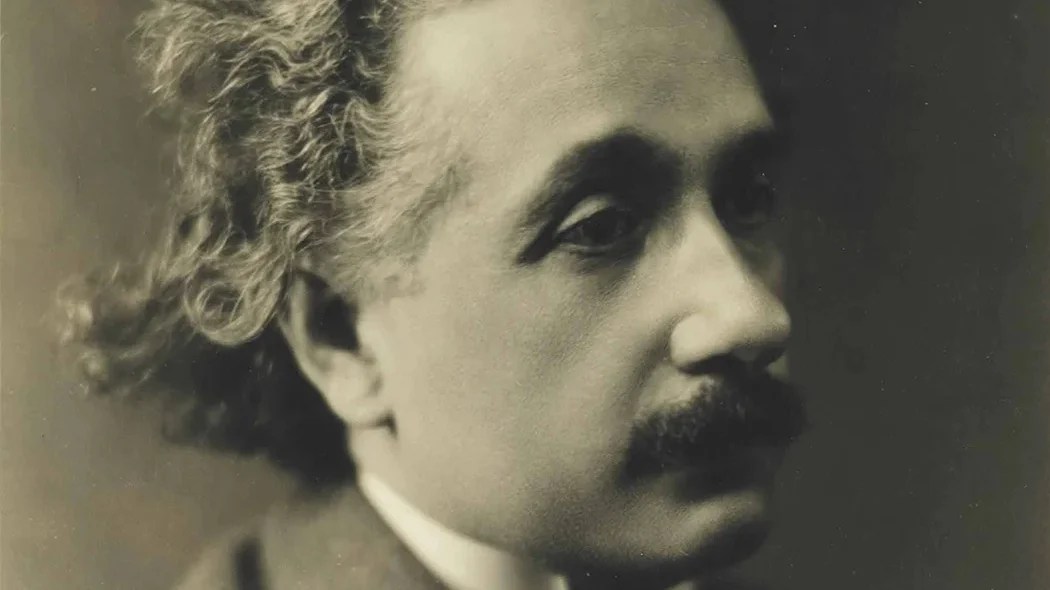
After Albert Einstein’s death in 1955, a pathologist—searching for the secret of genius—removed, dissected, and ultimately stole the mathematician’s brain.
In the ongoing battle against PTSD, a potential new weapon emerges: a nasal spray loaded with neuropeptide Y.
The idea that consciousness emerges naturally alongside intelligence could be an anthropocentric distortion.
Who — or what — really controls your mind?
New research shows that the transition from general to specific memories involves the maturation of inhibitory neurons in the hippocampus.
Walter Pitts rose from the streets to MIT, but couldn’t escape himself.
Brain activity may be more like “ripples in a pond” rather than signals sent on a telecommunications network.
Neuroscientist and author Bobby Azarian explores the idea that the Universe is a self-organizing system that evolves and learns.
Plato and Carl Sagan were wrong about the human brain, says a top neuroscientist.
▸
7 min
—
with
Neuroscientists and artists alike are making the case that we could transform the world through psychedelics.
A new study from Finland suggests that we all process the behavior of others using the same neural networks.
You’ve heard about your “lizard brain.” But what about the other two?
▸
8 min
—
with
Brain-computer interfaces could enable people with locked-in syndrome and other conditions to “speak.”
Evolutionary pressures drove the formation of tribes who encoded their values in myths and symbols. Was this cooperation cursed?
Memory, responsibility, and mental maturity have long been difficult to describe objectively, but neuroscientists are starting to detect patterns. Coming soon to a courtroom near you?
The dying brain experiences a surge of electrical activity. Could this help explain the mysterious phenomena of near-death experiences?
Emotion dysregulation has been linked to unhealthy risk-taking, relationship challenges, and negative physical health outcomes.
A recently identified stage of sleep common to narcoleptics is a fertile source of creativity.
Meditation can put you in a wiser relationship with life.
Desperate times call for desperate measures.
Thomas Edison was on to something…
Neuroscience is beginning to provide clues about the emergence of human consciousness.
The hallucinations that characterize schizophrenia may be due to a “reality threshold” that is lower than it should be.
People with aphantasia cannot conjure mental images, either original or from memory.
A recent study highlights the astounding adaptability of the human brain.
Despite a reputation for catastrophe and cat killings, curiosity is a beneficial drive that improves our lives and well-being.
Striking differences in the composition of the gut microbiome suggest that fermented food could help those suffering from anorexia.
Forgetting and misremembering are the building blocks of creativity and imagination.