The decentralized web will be as big a game changer as the internet was in the ’90s
- The internet has witnessed many big developments since it was created. The next big one will be decentralization.
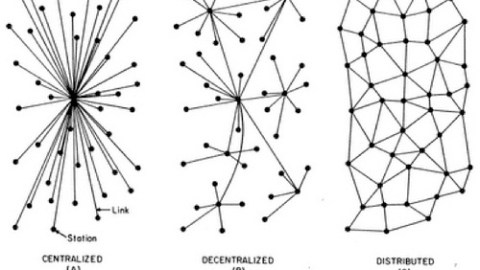
- Right now, the internet is centralized, which cause many issues, not the least of which is big companies having power over vast amounts of data.
- Over the past few years there has been a major increase in the number of decentralized projects working on making the decentralized web a reality in the near future.
We’ve come a long way since Tim Berners-Lee created the internet back in 1990.
What was once nothing more than a mere twinkle in his eye has become the center-point of the lives of millions of people all around the world.
From giving us instant access to information and helping us stay in touch with our friends and family members who live on the other side of the globe to helping us to do our weekly shopping without having to get out of bed and enabling us to collect and breed digital cats, the internet has enabled many changes — for better and for worse.
However, now that we seem to have understood more or less how and when to use the web, communication is about to change all over again.
‘Decentralization’ is the new big buzzword
We’ve made some rapid developments in technology over the past few years.
Artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and of course, cryptocurrencies, have been all over the headlines and have attracted a huge amount of attention as a result.
Now, the next step for the web is decentralization — and it’s kind of a big deal.
Why do we need a decentralized web?
With all our data in the hands of a small number of huge centralized corporations, we are at the mercy of hackers, increased surveillance, and increased censorship.
Since the recent reports of Google — a company that has always prided itself on bringing the fairest, most accurate search results in the world to its users — working on a censored search engine for China, there have been mounting concerns by human rights groups about the future of the web.
In an interview, Patrick Poon, a China researcher for Amnesty International, stated, “In putting profits before human rights, Google would be setting a chilling precedent and handing the Chinese government a victory.”
Considering how much of a monopoly Google currently has on the web (think YouTube, Google News, Google Maps, Google Drive and Google AdWords), such news is quite startling — and a little scary.
The big question many people are finding themselves asking is: What’s the alternative?
It turns out, an encrypted, blockchain-operated decentralized web could be the answer.
Who are the major companies involved?
Over the past couple of years, there has been a significant rise in the number of companies dedicating their time, money, and resources to creating decentralized alternatives for some of the most popular centralized products.
TRON is one of the projects dedicated to establishing a decentralized web.
As one of the largest blockchain-based operating systems in the world, it has high throughput and can currently support approximately 2,000 transactions per second, drastically surpassing the likes of Bitcoin and Ethereum, which can support only 3-6 transactions and 25 transactions per second respectively.
It also has high scalability and availability options which can support a huge number of users. The team’s overall long-term goal is to make decentralized software more versatile in order to, ultimately, expand the industry.
The TRON team is made up of over 100 experienced international blockchain enthusiasts, who have a significant amount of experience and have been employed by internet giants such as Alibaba, Tencent, and Baidu.
Earlier this year, TRON announced Project Atlas, in which they acquired file-sharing giant BitTorrent. The move marks the first major crossover between file sharing and decentralized technology, and has helped increase TRON’s profile.
Meanwhile, companies like Graphite Docs have made a decentralized alternative to Google Docs that encrypts all your work, files, and messages, while still making them shareable.
Unlike a centralized service where your private information is at the hands of the provider, the files stored on Graphite Docs are completely owned by the user.
Similarly, projects like Skycoin are developing the backbone of a new decentralized internet, with a mesh network that pays users for supporting it. The Skycoin project and specifically its leading product Skywire has over 9,500 nodes online. One of the project’s community members even built a dedicated page with a regularly updated map of all active nodes around the world.
Skywire’s current testnet has functions similar to TOR but is actually much faster. Community members can build and operate their own simple DIY nodes called ‘Skyminers’ to access and expand the mesh network. Soon, they will also be able to purchase officially sanctioned Skyminers from Skycoin’s website. During the testnet phase, running an approved Skyminer on the network earns Skycoin currency on a monthly basis. When mainnet launches these Skyminers will earn currency based on how much bandwidth they forward and process. This project, like many others with net-neutrality values at their core, is aiming to bring freedom and power back to the users and away from centralized, controlling ISPs and governments.
The future of the internet
We’re still a long way off complete decentralization, but the popularity of the concept is becoming increasingly apparent.
As the problems of centralization become more obvious, it’s likely that we’ll continue to see a huge push towards a decentralized future as we move further into 2019.
Cryptocurrencies have had their time in the spotlight but now it’s time to focus on solving bigger problems.






