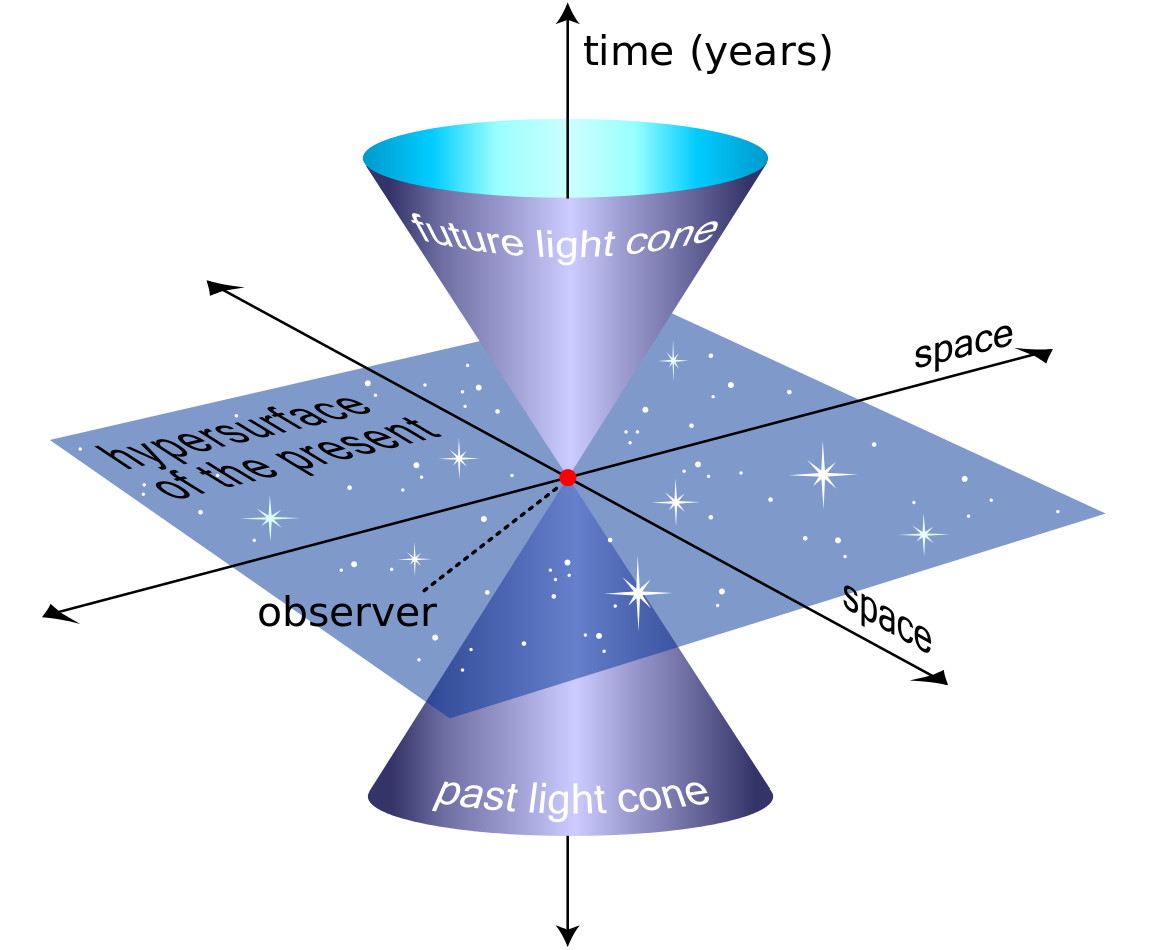
Will time run backward if the Universe collapses?

- In our Universe, time has been progressing forward, for all observers, ever since the inception of the hot Big Bang.
- There are a few “arrows of time” that coincide with this, including that the Universe has been expanding and, thermodynamically, that entropy has been increasing.
- If the Universe instead were to contract and collapse, could that lead to time running backward? It’s a question that puzzled even Stephen Hawking, but we can answer it today.
With each passing moment in the Universe, we’re constantly stepping forward in time. Each successive instant gives way to the next, with time continuously appearing to flow in the same direction — forward — without fail. And yet, it isn’t particularly clear exactly why this is the case. Still, if we look for it, we can find that a number of things also happen to always move in the same direction, from moment-to-moment, exactly the way time does. Objects move through the Universe proportional to their velocity. They change their motion due to the effects of gravity and the other forces. On large scales, the Universe expands. And everywhere we look, the entropy of the Universe always goes up.
As the story of our cosmic evolution continues, we think all of these things will continue: the laws of physics will still apply just as they do today, dark energy’s presence ensures that the Universe will keep on expanding, and entropy will keep increasing, as dictated by the laws of thermodynamics. Many have speculated — although there is no proof — that the arrow of thermodynamics and the arrow of time may be related. Still others have speculated that dark energy might evolve over time, rather than being a constant, leaving the door open to the possibility that it might someday counteract and reverse our Universe’s expansion. What happens, then, if we put these speculations together?
We’d wind up imagining that perhaps the Universe will cease expanding, that it will instead begin collapsing, and that we’d have to then ask whether this means that entropy could decrease and/or time could even start running backward? It’s a mind-bending possibility, and one for the laws of physics to answer. Let’s see what they have to say about it all!
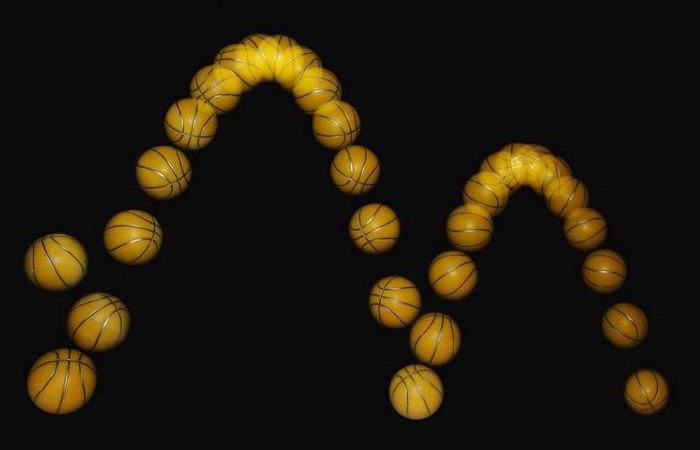
One of the most important symmetries in all of physics is known as time-reversal symmetry. Put simply, it says that the laws of physics obey the same rules whether you run the clock forward or backward. There are many examples where one phenomenon, if you run the clock forward, corresponds to an equally valid phenomenon if you run the clock backward. For example:
- A purely elastic collision, like two billiard balls colliding, would behave exactly the same if your ran the clock forward and backward, right down to the speed and angle that the balls will go off at.
- A purely inelastic collision, where two objects smash into each other and stick together, is exactly the same as a purely inelastic explosion in reverse, where the energy absorbed or released by the materials is identical.
- Gravitational interactions work the same forward and backward.
- Electromagnetic interactions behave identically forward and backward in time.
- Even the strong nuclear force, which binds atomic nuclei together, is identical forward and backward in time.
The lone exception, and the only known time where that symmetry is violated, occurs in the weak nuclear interaction: the force responsible for radioactive decays. If we ignore that outlier, the laws of physics truly are the same regardless of whether time goes forward or backward.
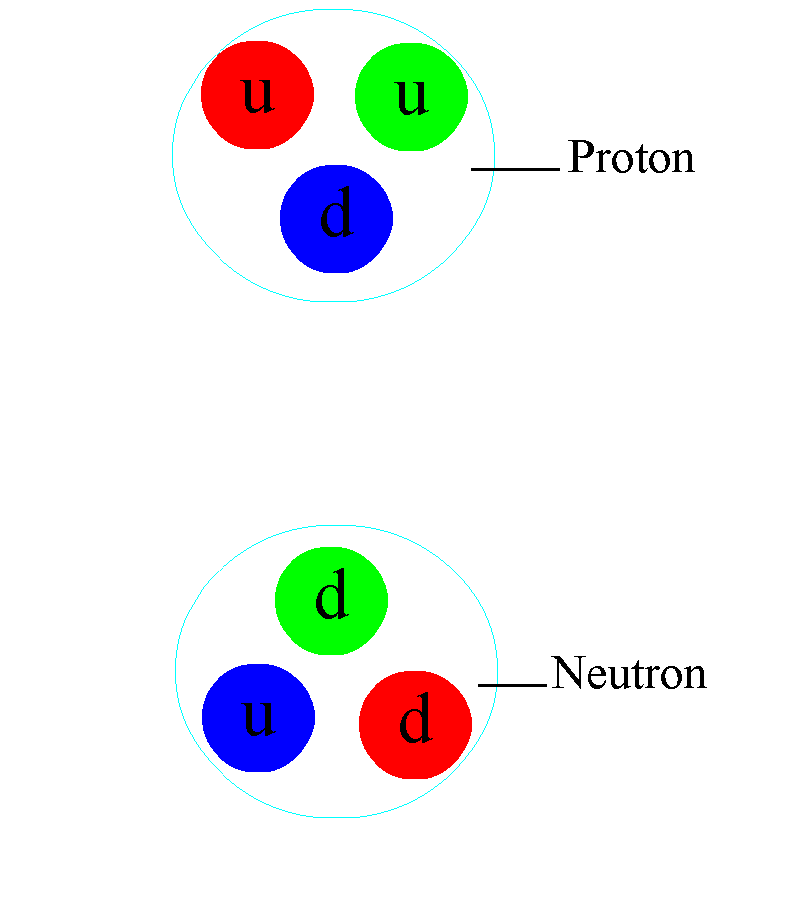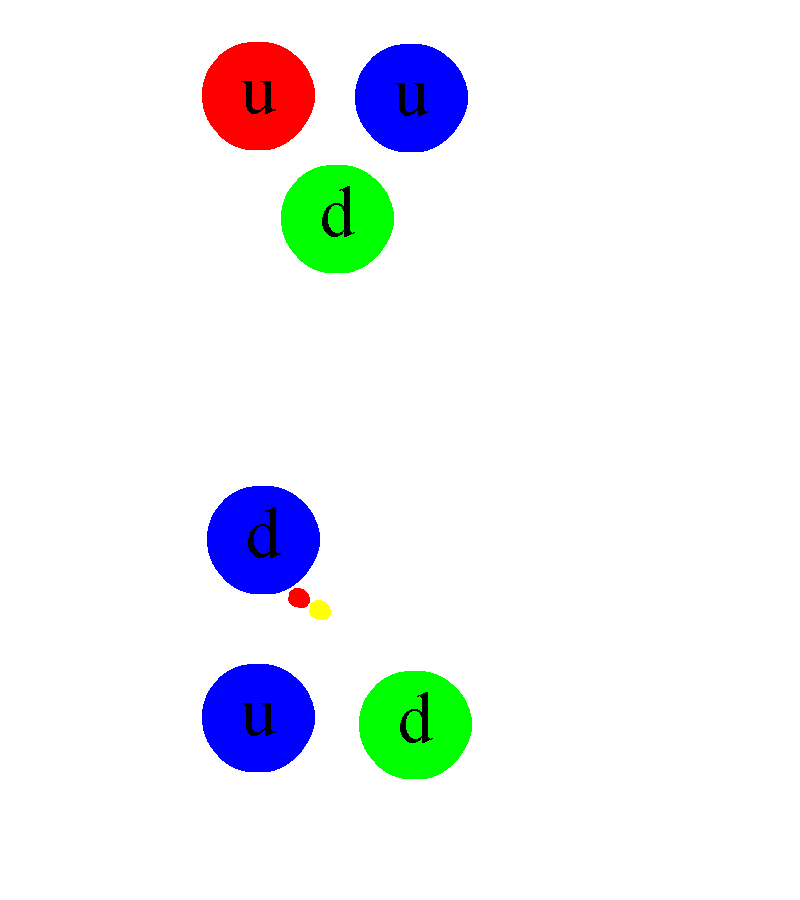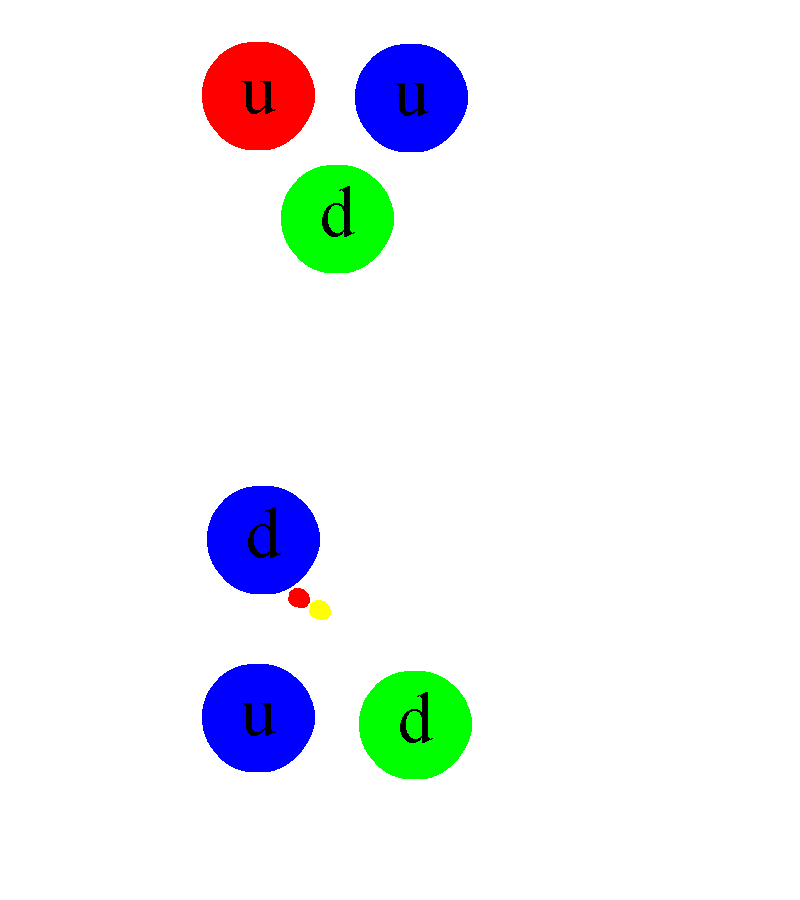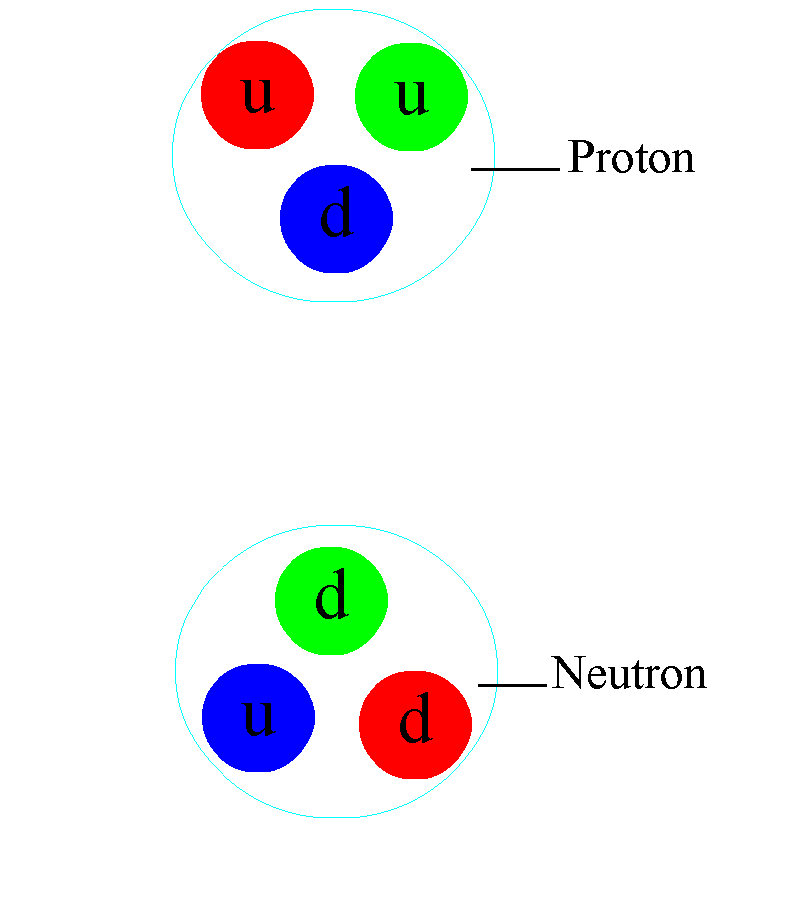
What this means is that, if you wind up at any final state at any moment in time, there’s always a way to get back to your initial state if you just apply the right series of interactions in just the right order. The only exception is that, if your system is complex enough, you’d have to know things like the precise positions and momenta of your particle to a better accuracy than is quantum mechanically possible. Leaving the weak interactions and this subtle quantum rule aside, the laws of nature really are time-reversal invariant.
But this doesn’t appear to be the case for everything we experience. Some phenomena clearly display an arrow of time, or a preference for a particular one-way direction. If you grab an egg, break it, scramble it, and cook it, that’s easy; you’ll never uncook, unscramble, and un-break an egg, though, no matter how many times you try. If you push a glass off the shelf and watch it shatter against the floor, you’ll never see those bits of glass rise up and spontaneously reassemble themselves. For these examples, there clearly is a preferred direction to things: an arrow in which things flow.

Admittedly, these are complex, macroscopic systems, experiencing an extremely intricate set of interactions. Nevertheless, the combination of all these interactions adds up to something important: what we know as the thermodynamic arrow of time. The laws of thermodynamics basically state that there are a finite number of ways that the particles in your system can be arranged, and the one(s) that have the maximum number of possible configurations — the one(s) in what we call thermodynamic equilibrium — are the ones that all systems will tend toward as time goes forward.
Your entropy, which is a measure of how statistically likely or unlikely a particular configuration is (most likely = highest entropy; very unlikely = low entropy), always rises over time. Only if you’re already in the most likely, highest entropy configuration already will your entropy stay the same over time; in any other state, your entropy will increase.
My favorite example is to imagine a room with a divider down the middle: with one side full of hot gas particles and the other full of cold gas particles. If you remove the divider, the two sides will mix and achieve the same temperature everywhere. The time-reversed situation, where you take a room of even temperature and stick a divider in the middle, spontaneously getting a hot side and a cold side, is so statistically unlikely that, given the finite age of the Universe, it never occurs.
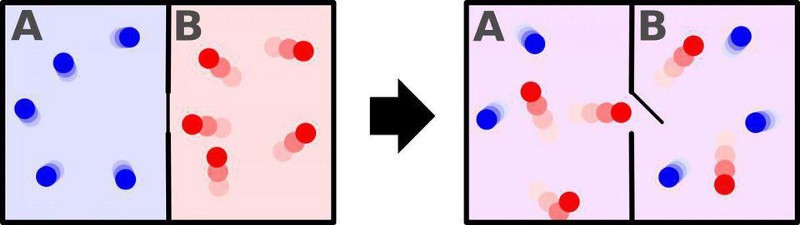
But what could occur, if you were willing to manipulate these particles intricately enough, is you could pump enough energy into the system to separate the particles into hot and cold, relegating one side to containing all the hot particles and the other into containing all the cold ones. This idea was put forth some 150 years ago, and goes all the way back to the person who unified electricity and magnetism into what we now know as electromagnetism: James Clerk Maxwell. It’s known, in common parlance, as Maxwell’s demon.
Imagine that you have this room full of hot-and-cold particles, and there is a central divider, but the particles are evenly distributed on both sides. Only, there’s a demon controlling the divider. Whenever a hot particle is going to smash against the divider from the “cold” side, the demon opens a gate, letting the hot particle through. Similarly, the demon also lets cold particles get through from the “hot” side. The demon has to put energy into the system to make this happen, and if you consider the demon to be part of the box/divider system, the total entropy still goes up. However, for the box/divider alone, if you were to ignore the demon, you’d see the entropy of just that box/divider system go down.
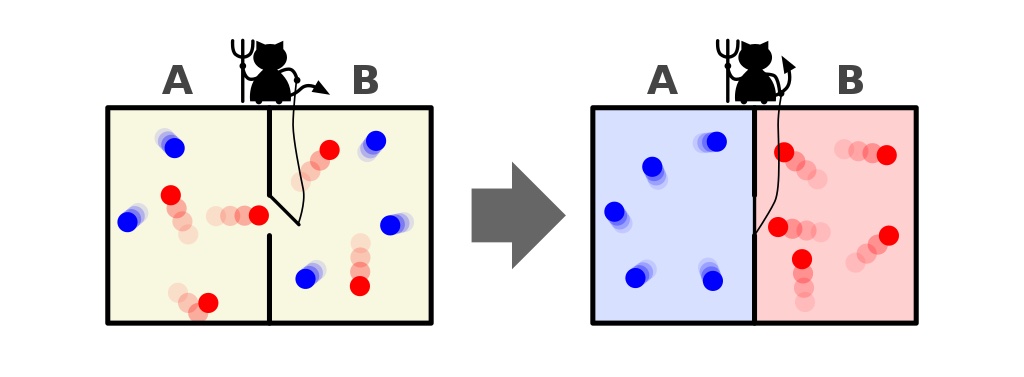
In other words, by manipulating the system appropriately from the outside, which always involves pumping energy from outside the system into the system itself, you can cause the entropy of this non-isolated system to artificially decrease.
The big question, before we even get to the Universe, is to imagine that along with these hot and cold particles, there’s also a clock inside the system. If you were inside the system, had no knowledge of the demon, but saw the gate opening and closing rapidly in various places — seemingly at random — and experienced one side of the room getting hotter while the other got colder, what would you conclude?
Would it appear that time was running backward? Would the hands on your watch start ticking backward instead of forward? Would it appear to you that the flow of time had reversed itself?
We’ve never performed this experiment, but as far as we can tell, the answer ought to be “no.” We have experienced conditions where entropy:
- increased rapidly,
- increased slowly,
- or remained the same,
both in systems on Earth and for the Universe as a whole, and as far as we can tell, time continues to always march forward at the same rate it always does: one second per second.
In other words, there is a perceived arrow of time, and there is a thermodynamic arrow of time, and they both always point in the forward direction. Is this causation? While some — notably Sean Carroll — speculate that they are linked in some fashion, we should remember that is pure speculation, and that no link has ever been uncovered or demonstrated. As far as we can tell, the thermodynamic arrow of time is a consequence of statistical mechanics, and is a property that emerged for many-body systems. (You might need at least three.) The perceived arrow of time, however, seems largely independent of anything entropy or thermodynamics may do.
What, if anything, happens when we bring the expanding Universe into the equation?
It’s true that, for all of time since (at least) the hot Big Bang, the Universe has been expanding. It’s also true that while time is linear, passing at that constant perceived rate of one second per second, the rate at which the Universe expands is not. The Universe expanded much more quickly in the past, is expanding more slowly today, and will asymptote to a finite, positive value. This, as far as we understand it, means that distant galaxies that aren’t gravitationally bound to us will continue to recede from our perspective, faster and faster, until what remains of our Local Group is the only remaining thing we can access.
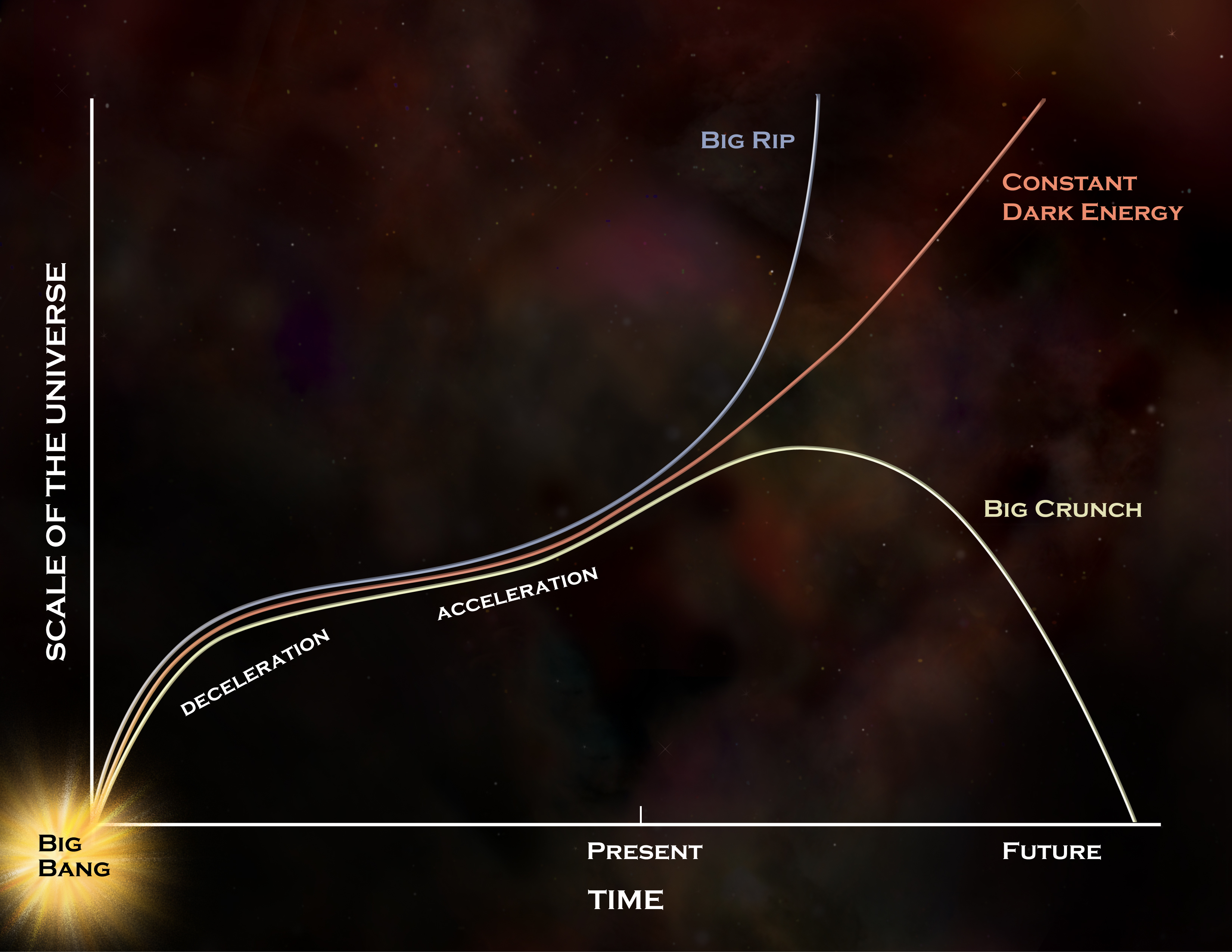
But what if this weren’t the case? What if, as in some theoretical variants of evolving dark energy, the expansion were to continue to slow down, eventually stop altogether, and then gravity would cause the Universe to contract? It’s still a plausible scenario, although the evidence doesn’t point to it, and if it pans out, the Universe could still end in a Big Crunch in the far future.
Now, if you take an expanding Universe and apply that earlier symmetry to it — time-reversal symmetry — you’ll get a contracting Universe out of it. The reverse of expansion is contraction; if you time-reversed the expanding Universe, you’d get a contracting Universe. But within that Universe, we have to look at the things that are still happening.
Gravitation is still an attractive force, and particles that fall into (or form) a bound structure still exchange energy and momentum through elastic and inelastic collisions. The normal matter particles will still shed angular momentum and collapse. They will still undergo atomic and molecular transitions and emit light and other forms of energy. To put it bluntly, everything that makes entropy increase today will still make entropy increase in a contracting Universe.
So if the Universe contracts, entropy will still go up. In fact, the biggest driver of entropy in our Universe is the existence and formation of supermassive black holes. Over the history of the Universe, our entropy has increased by about 30 orders of magnitude; the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way alone has more entropy than the entire Universe had just 1 second after the hot Big Bang!
Not only would time continue to run forward, as far as we know, but the instant that preceded the Big Crunch would have enormously more entropy than the Universe did at the start of the hot Big Bang. All the matter and energy, under those extreme conditions, would start to merge together as all the supermassive black holes had their event horizons begin to overlap. If there were ever a scenario where gravitational waves and quantum gravitational effects could show up on macroscopic scales, this would be it. With all the matter and energy compressed into such a tiny volume, our Universe would form a supermassive black hole whose event horizon was billions of light-years across.
What’s interesting about this scenario is that clocks run differently when you’re in a strong gravitational field: where you’re at small enough distances from a large enough mass. If the Universe were to recollapse and approach a Big Crunch, we’d inevitably find ourselves approaching the edge of a black hole’s event horizon, and as we did, time would begin dilating for us: stretching our final moment out toward infinity. There would be some sort of race occurring as we fell into a black hole’s central singularity, and as all the singularities merged to lead to the ultimate demise of our Universe in a Big Crunch.
What would happen after that? Would the Universe simply wink out of existence, like a complicated knot that was suddenly manipulated in such a way that it came undone? Would it lead to the birth of a new Universe, where this Big Crunch would lead to another Big Bang? Would there be some sort of cutoff, where we’d only get so far into the crunch scenario before the Universe rebounded, giving rise to some sort of rebirth without reaching a singularity?
These are some of the frontier questions of theoretical physics, and while we don’t know the answer, one thing seems to be true in all scenarios: the entropy of the entire Universe still increases, and time always runs in the forward direction. If this turns out not to be correct, it’s because there’s something profound that remains elusive to us, still waiting to be discovered.