In a video lesson, Neil Irwin emphasizes that while data is the 21st century’s currency, mastering its interpretation and application can enhance both individual and organizational success, urging professionals to leverage data wisely for career development.
Natalie Nixon emphasizes the importance of cultivating creativity quotients (CQs) in organizations, alongside IQ and EQ, by integrating gratitude, humility, curiosity, empathy, and action to enhance problem-solving and foster productive interactions.
Machine-learning consultant Eric King cautions against exaggerating AI’s capabilities, while predictive AI expert Eric Siegel emphasizes that successful AI pitches should prioritize concrete business value, focus on deployment goals, and engage stakeholders through impactful demonstrations rather than just technology details.
Predictive analytics expert Eric Siegel highlights that algorithms, often trained on flawed human data, can perpetuate biases, influencing critical decisions like resource access, and emphasizes the need for awareness and responsible practices to mitigate these social justice risks.
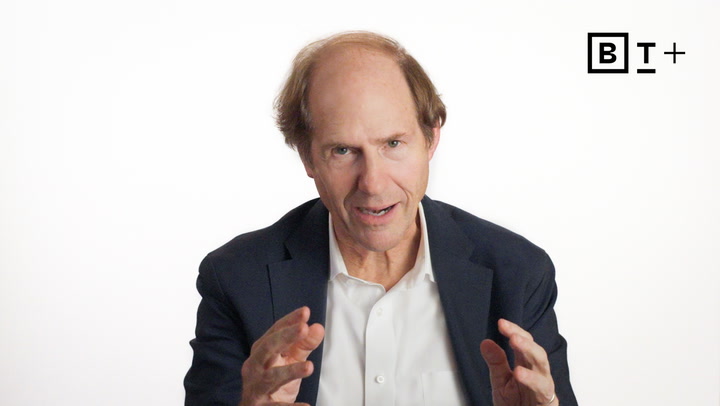
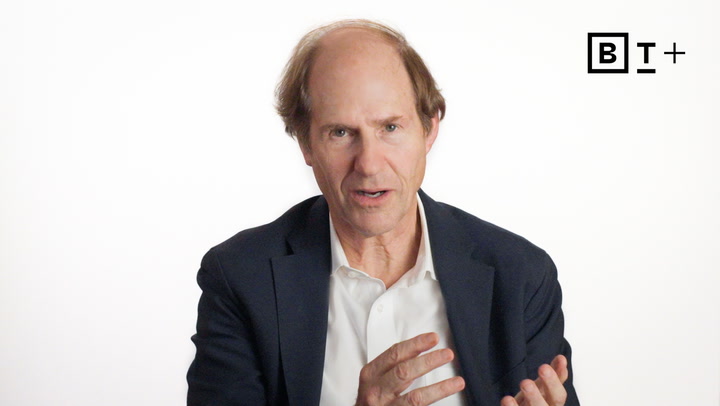
Predictive analytics expert Eric Siegel emphasizes that successful machine learning projects require a strong foundation in business goals and collaboration between data scientists and stakeholders, advocating for his bizML framework to ensure effective deployment and continuous model improvement.
Predictive analytics expert Eric Siegel emphasizes that successful machine learning projects require alignment between business stakeholders and data scientists, urging both sides to bridge their knowledge gaps to enhance project deployment and operational improvements.
Machine learning, a branch of artificial intelligence, transforms raw data into predictive models that drive business decisions, exemplified by UPS’s use of predictive analytics to optimize delivery routes, saving $350 million annually and reducing emissions.
Generative AI is impressive but overhyped, as experts like Eric Siegel argue that its tendency to hallucinate makes predictive AI a more reliable choice for automating large-scale operations.
In a crisis, trust, resilience, and accountability are essential, as emphasized by CEO and former Navy SEAL Brent Gleeson, who believes that cultivating a strong culture is key to achieving these qualities.
Paradigm shifts, like those introduced by Copernicus, Newton, and Darwin, also affect economies, with innovation consultant Rita McGrath highlighting the rise of stakeholder capitalism and consumer protection concerns, urging businesses to adapt to these emerging signals for long-term success.
Cultural psychologist Michele Gelfand illustrates that a system’s tightness or looseness correlates with the threats it faces, and understanding this framework can enhance collaboration, reduce tensions, and improve organizational health.
Hierarchies, while efficient for large-scale decisions, often fail to motivate employees, prompting Toyota in the 1980s to adopt a “lean” management philosophy that empowers workers to solve problems, leading to greater efficiency and innovation.
Innovation thrives on audacious ambition rather than incremental steps; in his video lesson, Charles Duhigg emphasizes that starting with “stretch goals” can inspire revolutionary change by encouraging a fresh perspective on challenges.
Professor Michael Watkins emphasizes that organizations should be analyzed by focusing on key components—strategy, structure, systems, talent, incentives, and culture—to identify interdependencies and drive improvement, similar to how one would examine an airplane engine by its essential parts.
In response to the Suez Canal blockage in March 2021, Professor Michael Watkins emphasizes that leaders can enhance their strategic thinking skills—through pattern recognition, systems analysis, mental agility, structured problem-solving, visioning, and political savvy—to better navigate the complexities of global trade disruptions.
In this video lesson, Professor Michael Watkins outlines six key disciplines of strategic thinking that can benefit anyone aspiring to lead, emphasizing their role in recognizing opportunities, prioritizing actions, and mobilizing resources for career growth.
Strategic thinking, as defined by Michael Watkins, involves critically and creatively envisioning potential futures beyond the current situation, and he outlines six specific disciplines to intentionally cultivate this mindset.
Professor Cass Sunstein highlights that “sludge,” or bureaucratic frictions like excessive paperwork and waiting times, hinders access to benefits, and suggests conducting a sludge audit to streamline workflows and improve quality of life by identifying and reducing these inefficiencies.
In this video lesson, Professor Cass Sunstein explores the concept of “sludge”—the bureaucratic obstacles that hinder access to essential services—using Kafka’s “The Trial” and a COVID-19 case study to illustrate how reducing these barriers can improve people’s lives.
In a video lesson, Professor Cass Sunstein discusses how bureaucratic delays, termed “sludge,” hinder our access to desired services and offers strategies for organizations to minimize these frictions, ultimately reclaiming valuable time for individuals.
Professor Cass Sunstein defines “sludge” as the unnecessary bureaucracy and frictions, like long wait times and excessive paperwork, that hinder access to desired outcomes, suggesting organizations can improve experiences by minimizing these obstacles.
Businesses must recognize their profound responsibilities to society when engaging with AI, as its influence on privacy and decision-making can reshape industries and everyday life, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of various fields to anticipate potential consequences.
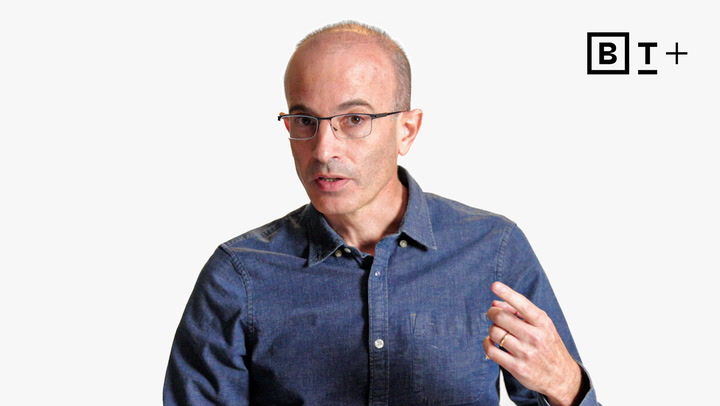
In a video lesson, Professor Yuval Harari emphasizes that, like children learning to walk, AI development requires self-correcting mechanisms and collaborative efforts among institutions to effectively manage risks and address potential dangers as they arise.
Professor Yuval Harari discusses how AI’s relentless, “always-on” nature contrasts with human needs for rest, potentially disrupting our daily rhythms, privacy, and decision-making processes as power shifts from humans to machines.
In this video lesson, Professor Yuval Harari explains that true AI, unlike basic automation, evolves by learning from habits to offer unparalleled customization, such as a coffee machine that predicts your preferences and even invents new drinks.
The emergence of AI like AlphaGo, which developed unexpected strategies in the ancient game of Go, challenges our understanding of machines as mere tools, prompting profound questions about coexisting with an intelligence that can create and innovate beyond human comprehension.
Brené Brown and Amy Edmondson emphasize that embracing failure fosters innovation and creativity, advocating for a culture of shared awareness and psychological safety where failures are normalized, celebrated, and approached with empathy and humility.
Harvard researcher Amy Edmondson emphasizes that while quick decisions during disruptions may seem necessary, adopting a systems thinking approach can transform these challenges into valuable learning opportunities, fostering synergy and proactive experimentation within organizations.
Harvard researcher Amy Edmondson suggests that while failure is often viewed negatively, some mistakes can be beneficial, and we can learn to avoid or mitigate unfavorable errors by adopting a smarter approach to failure.
Tiffani Bova emphasizes that fostering employee satisfaction is crucial for enhancing customer experience, advocating for the integration of customer experience (CX) and employee experience (EX) to achieve predictable growth.